|
In our previous post, we shared about 5 water purification methods that you can use to obtain clean drinking water.
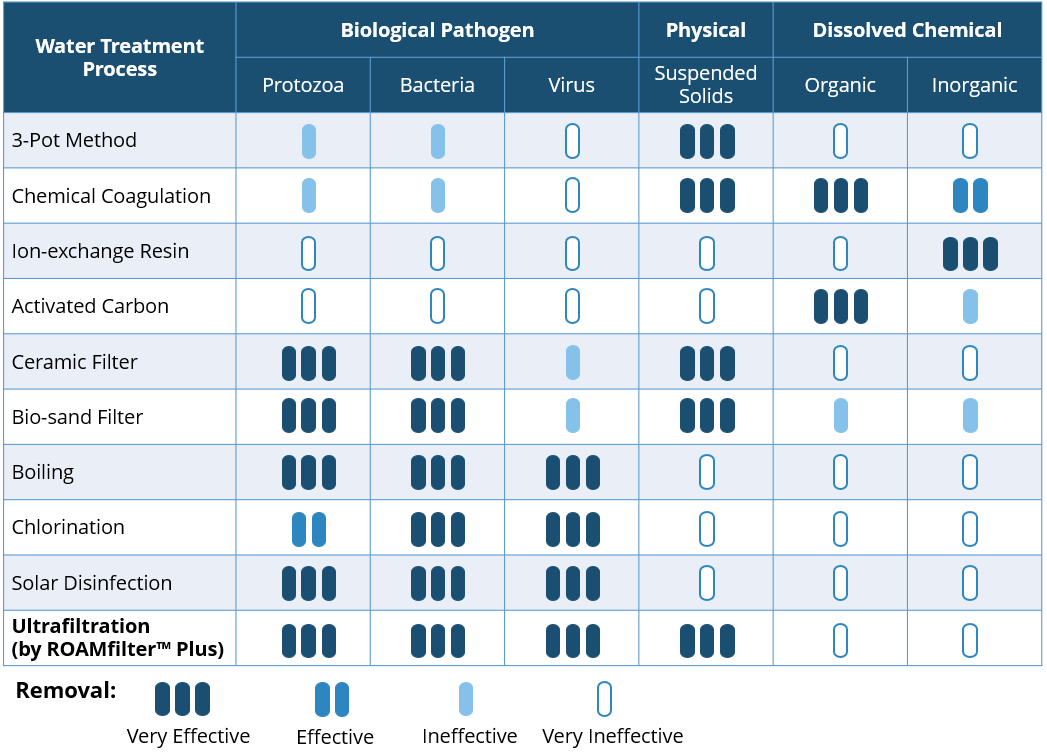
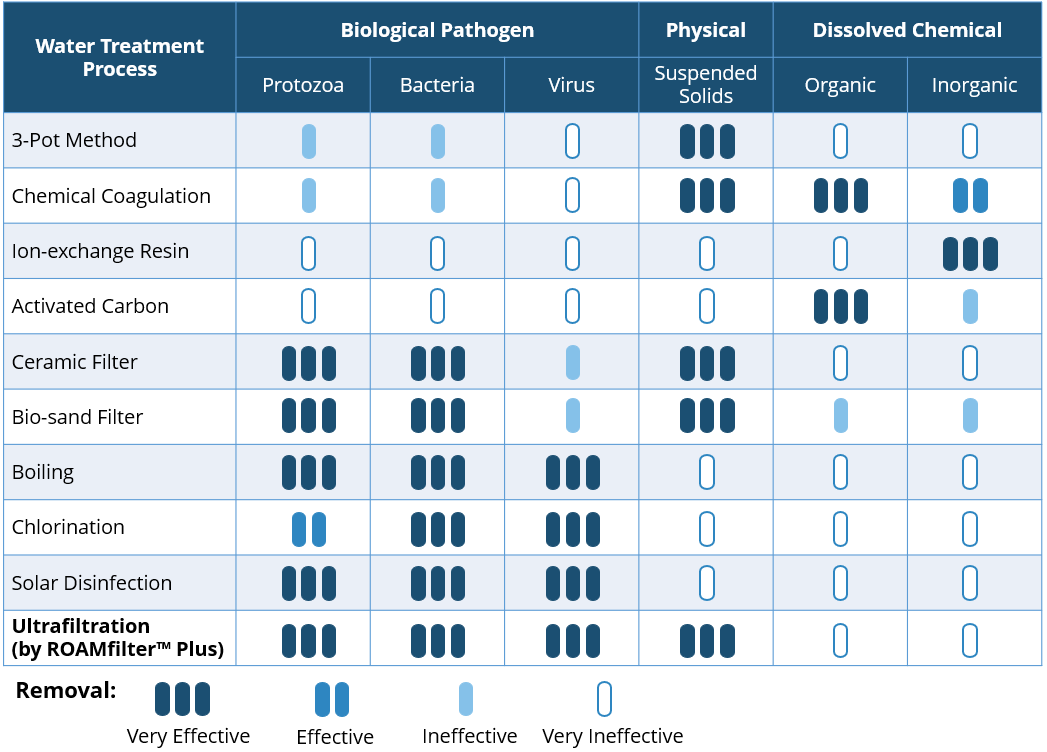
We know that you are thirsty for more, so here are 5 more low-cost water treatment methods that will prove useful in rural areas. SummaryCeramic Filter
Slowly but surely, I’m filtering your water
Source: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/518125132109352567/?lp=true
Ceramic filters are commonly used in remote parts of the world to treat water in households. A ceramic filter has fine micro-pores that can mechanically remove suspended particles when water flows through it via gravity.
The filter may be coated with colloidal silver, which acts as a disinfectant to kill pathogens. However, the filter can be clogged easily, especially if the inlet water is turbid. While the inner surface of the ceramic filter can be scrubbed to remove the impurities trapped, this maintenance method is limited in its effectiveness.
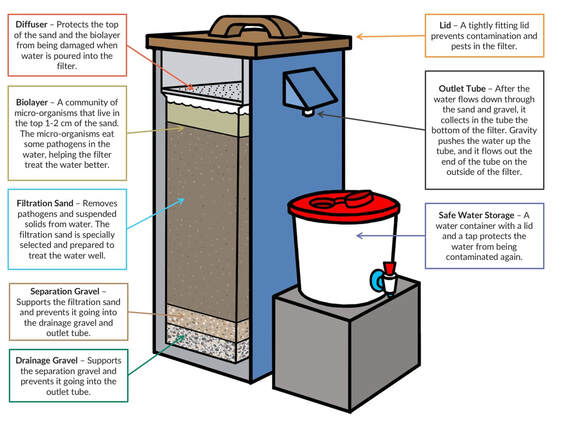
Bio-sand Filter
I have a highly layered personality…I mean structure
Source: https://www.cawst.org/services/expertise/biosand-filter/more-information
Bio-sand filter has the advantage of material simplicity and is typically made up of sand and gravel. It utilizes a mechanical and biological process to treat the water.
The microorganisms establish a community on the top layer of sand (biofilm) and cleans the water by “eating” the organic and inorganic particles as it flows through the system. Due to insufficient oxygen in the middle of the filter, most microbes will only grow on the top layer of sand, keeping it safely separated from the effluent (out-put) water. A well-built bio-sand filter is typically able to remove about 98 to 99% of bacteria and protozoa, but is less effective for viruses and is unable to remove dissolved contaminants such as salts, arsenic and fluoride. The removal of organic and inorganic particles through biofilm may be limited as biochemical reduction is highly dependent on the contact time and density of the biofilm; increasing both factors will also reduce the flow rate of the filter. Maintenance can be tricky as the filter may stop working when the biofilm becomes too thick and dense. To recover the system, scrape away the top few centimeters of sand to reduce the thickness of the biofilm.
Boiling
Hot.
Source: https://www.wonderopolis.org/wonder/why-does-water-bubble-when-it-boils
Boiling is an effective method to destroy most biological pathogens and most of us still boil our water even if we have other water treatment solutions.
The water should be brought to a rolling boil for at least 5 minutes and preferably up to a period of twenty minutes. Longer boiling time is needed at higher elevations to ensure all the pathogens are destroyed. Prior filtration is usually needed because any particles in the water can provide a hiding place for bacteria, protecting them from the heat. Basically, brown water remains brown, even after intense boiling. Boiling can affect the taste of water due to the loss of oxygen in it. The taste can be improved by re-oxygenizing it through vigorously stirring or shaking the water.
Sign up for our newsletter!
 
Chlorination
Staying behind for residual disinfection
Source: https://www.gettyimages.com/detail/photo/effervescent-tablets-in-water-high-res-stock-photography/594844889
Chlorination is the most common disinfection method used in water treatment plants and in our swimming pools. Chlorine is widely used because it is relatively low-cost and effective in destroying biological pathogens.
It is most commonly available in the form of liquid bleach (sodium hypochlorite) and chlorine tablets. The active component in chlorine disinfectant is the hypochlorite ion (OCL-), which oxidizes the cellular structure of germs and kills them in the process. For untreated water with low turbidity, dosing the water with appropriate amounts of chlorine and giving the hypochlorite ions a minimum contact time of 30 minutes can improve the quality of water tremendously. Chlorination works for most pathogens with the exception of some protozoa due to their protective cysts (thick outer shell). To ensure potability (drinkability), the protozoa needs to be removed by other means such as filtration. The dosage of chlorine also needs to be adjusted appropriately to ensure proper disinfection. Too little chlorine may result in incomplete disinfection while too much chlorine may affect the water's taste.
Solar Disinfection
Sun day fun day
Source: https://www.scidev.net/global/water/news/mistrust-slows-spread-solar-disinfection-tech.html
Solar disinfection (SODIS) is a simple and effective way to kill microorganisms in water. The only materials needed are transparent bottles and sunshine, which can be obtained easily,
SODIS uses heat and ultraviolet (UV) radiation to destroy pathogens. However, the water has to be clear because suspended solid particles can block the UV rays and reduce its effectiveness. The water should be exposed to strong sunlight for about five hours to destroy all pathogens. But if the water temperature rises to 50°C, the exposure period can be shortened to one hour.
Source: https://bluesolarcity.com/guide-solar-disinfection-sodis/
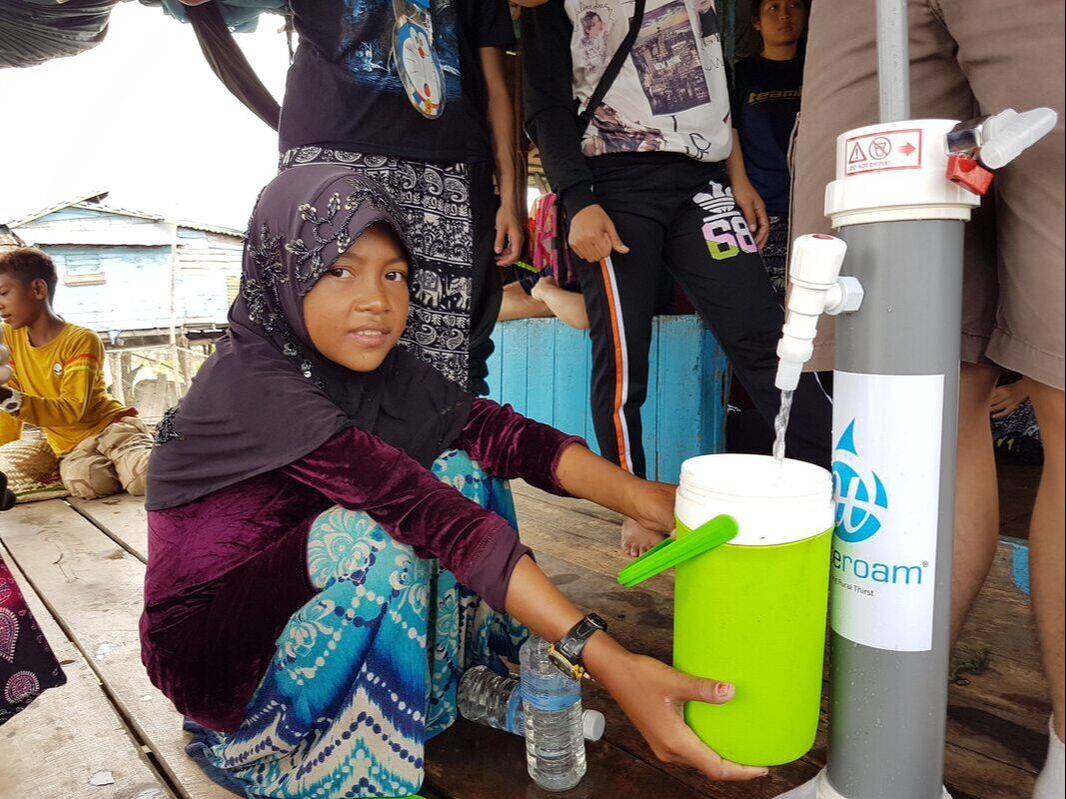
Ultrafiltration (by ROAMfilter™ Plus)
1L of water in seconds!
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a process that physically separates microscopic particles from the water based on the principle of size-exclusion. UF removes essentially all colloidal particles (0.01 to 1.0 microns) from water and some of the largest dissolved contaminants.
The ROAMfilter™ Plus is a water filtration system that is specifically made for disaster and rural development areas. The filter is designed to be safe, simple and swift. Safe because our technology utilizes 0.02-micron pore membranes, capable of removing bacteria and viruses. Simple because it works exactly like a bicycle pump, making it easy to operate and maintain without electricity. And Swift because at a light weight of 3 kg, it can be easily carried over any terrain and deployed to produce more than 200 litres of clean water per hour.
Missed Part 1 of this article?
Check out 10 simple life-saving methods for water purification (Part 1) to catch up on what you missed!
Did you know, 525,000 children under 5 die from diarrhoeal diseases every year? Millions more fall ill due to water-borne diseases caused by the lack of access to clean drinking water.
Please select the drop-down for other amounts
*Please refer below for terms and conditions
Let's build a world without prolonged thirst together!
Wateroam works with Sponsors & Champions to provide clean drinking water access. Through complementing one another's strengths, we are able to maximise our resources and increase social impact.
Sponsors provide resource support to empower Champions to deploy clean drinking water. Champions are those on the ground, actively working with communities in need of clean water. By working together, we can reach out rapidly to the 633 million people globally without safe water access. Visit our Get Involved section to learn how you can play a role! Blog Author: Ze Yong Yeoh
50 Comments
Do you know that 1 in 7 globally are consuming unsafe drinking water?
In fact, having clean drinking water is one of the biggest concerns for travelers living abroad, especially humanitarian workers and emergency relief organisations responding to disasters. Imagine being stranded after a flood swept through the city. The pipelines are broken and the water supply is disrupted. There is no power supply nor electricity. People around you are thirsty and in desperate need of clean water. With the limited resources available, how can you obtain safe drinking water?
Lucky for you, there are several simple methods you can use to purify water.
In this post, we will explore the advantages and drawbacks of the different water treatment methods and how we can treat and obtain clean drinking water in rural and disaster affected areas.
Summary
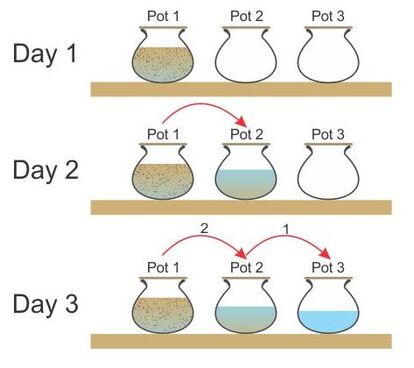
3-Pot Method
An affordable pre-treatment method!
Source: http://www.vicharoo.com/water/low-cost-water-purification-methods-1/
The 3-pot method is a simple trick you could do to improve your water quality with just a few pots. All you need is a clean cloth and three containers with cover. While this is by no means a complete disinfection, it reduces the larger physical suspended solids and provides you an improved source of water for emergency.
By storing water in a covered pot for at least two days in a safe and undisturbed condition, the process slows down bacteria growth and multiplication by depriving them of key respiratory elements such as oxygen. The process can reduce the level of aerobic bacteria by 50% due to the unfavorable survival conditions in the pot. Pathogens attached to suspended solids will also settle to the bottom of the pot with time, thereby improving the quality of the stored water. Always draw the supernatant (water from the top of the pot) to get cleaner water. The pots should be covered to avoid re-contamination and with a wide enough neck to ease the cleaning process. Pro-tip: The 3-pot method is a handy technique is commonly used as a form of pre-treatment before filtration!
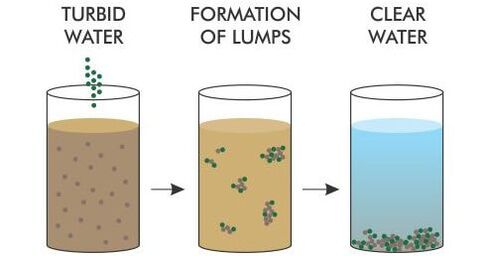
Chemical Coagulation
Coagulant to suspended particles: Let’s stick together
Source: http://www.vicharoo.com/water/low-cost-water-purification-methods-1/
Coagulation is a like using a “glue” to stick small particles together to form larger particles. The larger particles can then settle down faster because they are heavier.
Coagulants is the “glue” mentioned in the coagulation process. It includes aluminum or iron salts, such as ferric sulphate, ferric chloride, aluminum sulphate or polymers. But what’s the science behind this… “gluing” process? Interestingly, it is through the neutralization of the negatively charged suspended particles in the water. Coagulant turns the repulsion between particles to attraction and helps to bind the particles together. This could be done by stirring the coagulant in the water for a few minutes and letting the water to stand until most of the coagulated particles settle. Obtain the clear water from the top portion of the container. You can remove most organic compounds effectively by coagulation, while certain inorganic compounds, such as arsenic, lead, cadmium, mercury and copper could be removed as well.
Ion-exchange Resin
Stripping off the bad stuff
Source: https://www.dhgate.com/wholesale/reverse+osmosis+water+systems.html
As much as possible, we want to avoid a water source that is contaminated with heavy metals. Heavy metals that goes beyond the WHO threshold is harmful and chronic exposure can damage the human body indefinitely.
Passing the water through an ion-exchange resin is an effective way to remove inorganic chemicals including heavy metals. The resins act as a medium for ion exchange and when water contacts the resin, certain “bad” ions (such as heavy metals) are trapped and replaced by the ions not harmful to the human body. Anion resins and cation resins are the two most common resins used in the ion-exchange process. Anion resins attract negatively charged ions, while cation resins attract the positively charged ions. However, some contaminants are not easy to remove by conventional ion exchange resins. Specific resins have been developed to remove those contaminants. The most common chemical composition of ion-exchange resins is polystyrene, while certain types are manufactured from acrylic (either acrylonitrile or methyl acrylate).
Sign up for our newsletter!
 
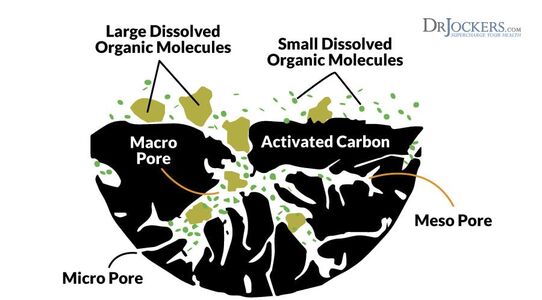
Activated Carbon
Adsorbing the organics
Source: https://drjockers.com/4-reasons-use-activated-charcoal/
Activated carbon is an effective material to remove organic chemicals from water besides coagulants. Activated carbon has many small pores on the surface to achieve a very high surface area and contact point.
One gram of powdered activated carbon has a surface area of more than 3,000 m². Thus, large amount of soluble substance can stick (adsorb) onto the activated carbon surface. Sufficient contact time (10 to 20 minutes) is usually required to remove contaminants effectively from the water. Although it is not effective for microbial contaminants, metals, nitrates and other inorganic contaminants, activated carbon can be combined with other treatment methods to complement each other.
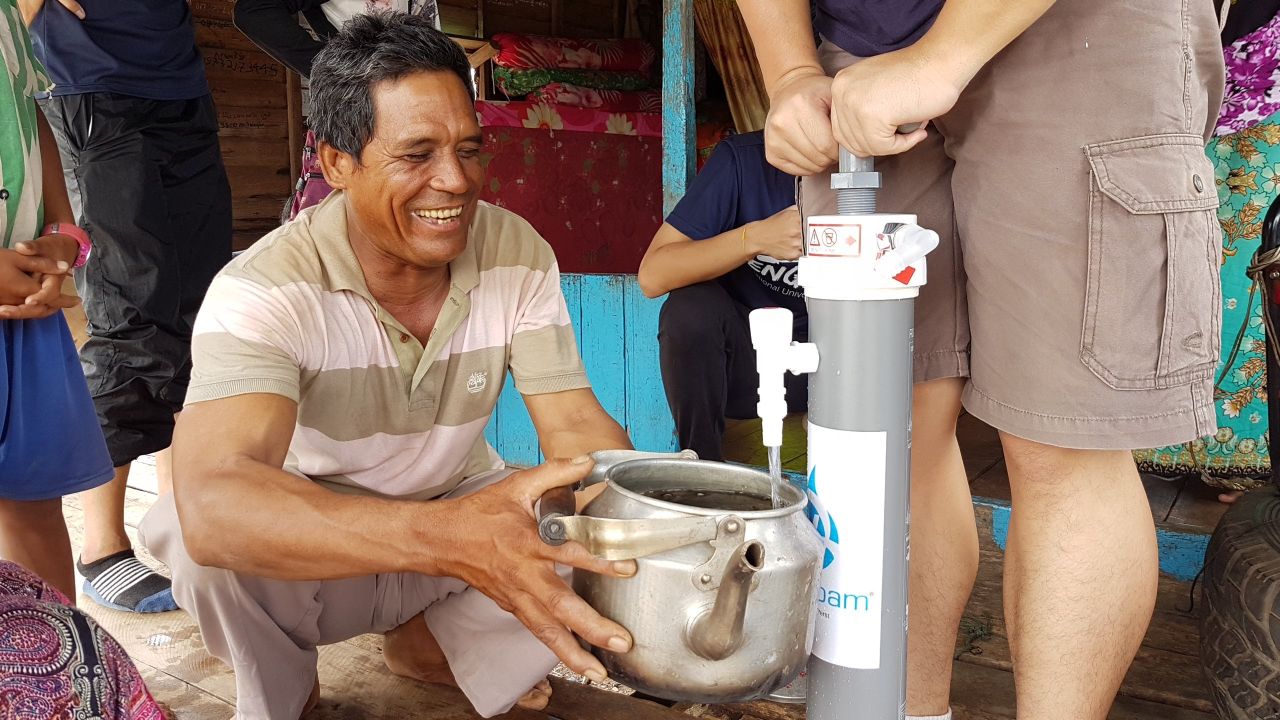
Ultrafiltration (by ROAMfilter™ Plus)
1L of water in seconds!
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a process that physically separates microscopic particles from the water based on the principle of size-exclusion. UF removes essentially all colloidal particles (0.01 to 1.0 microns) from water and some of the largest dissolved contaminants.
The ROAMfilter™ Plus is a water filtration system that is specifically made for disaster and rural development areas. The filter is designed to be safe, simple and swift. Safe because our technology utilizes 0.02-micron pore membranes, capable of removing bacteria and viruses. Simple because it works exactly like a bicycle pump, making it easy to operate and maintain without electricity. And Swift because at a light weight of 3 kg, it can be easily carried over any terrain and deployed to produce more than 200 litres of clean water per hour.
Thirsty for more knowledge?
Check out 10 simple life-saving methods for water purification (Part 2) to find out more!
Did you know, 525,000 children under 5 die from diarrhoeal diseases every year? Millions more fall ill due to water-borne diseases caused by the lack of access to clean drinking water.
Please select the drop-down for other amounts
*Please refer below for terms and conditions
Let's build a world without prolonged thirst together!
Wateroam works with Sponsors & Champions to provide clean drinking water access. Through complementing one another's strengths, we are able to maximise our resources and increase social impact.
Sponsors provide resource support to empower Champions to deploy clean drinking water. Champions are those on the ground, actively working with communities in need of clean water. By working together, we can reach out rapidly to the 633 million people globally without safe water access. Visit our Get Involved section to learn more about how you can play your part! Blog Author: Ze Yong Yeoh
Source: https://www.gettyimages.com/
Have you read the latest news about faecal bacteria found in bottled water?
Or hear about how water-related diseases caused millions to die in developing countries? Knowing what is in your water is no easy task. With so many contaminants in the water, knowing where to start is often the biggest challenge for most people. Therefore, it is extremely important for you to know what is in your water, especially for water sources in rural areas.
Source: https://www.reuters.com/
Advanced diagnostic tools are often needed to detect the tiny contaminants in the water, but these tools may not be the most accessible and feasible on the ground.
However, there are still low-cost methods you can use to detect the presence of pathogens in your water. Before we get there, let me first introduce 5 key water quality indicators, to help you determine whether your water source is suitable for drinking.
Turbidity
Source: https://savetheirl.org/irl-health-update/turbidity-targets/
Turbidity (cloudiness of water) is caused by colloidal matter or suspended particles that block light transmission through the water.
High turbidity is often associated with the presence of biological contamination, due to the tendencies of bacteria and pathogens adhering to the surface of solid particles. Turbidity also creates a challenge for water treatment methods, such as solar disinfection (SODIS), boiling or chemicals that aim to destroy microbes. Turbidity can indicate: Physical and Biological contamination Colour
Drinking water should ideally have no visible colour. The colour of the water is usually caused by the presence of dissolved material or suspended solids. It also indicates the possibility of the presence of coloured organic matter or metals.
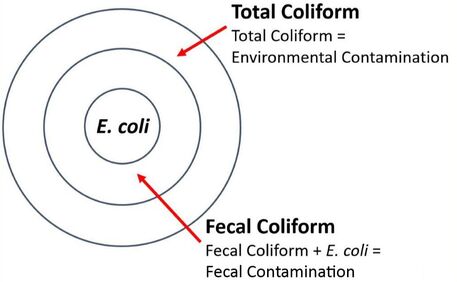
The presence of iron can be easily identified by the reddish colour in water. In addition, the water will also have a distinctive metallic taste (or “bloody” taste) which is unpalatable. While iron is an essential part of human nutrition, taking it in excess can affect the human body adversely. Colour can indicate: Physical, Biological and Chemical contamination Total coliform
Source: https://ietbuildinghealth.com/blog/sewage-testing-methods/total-and-fecal-coliform/
Total coliforms include bacteria that are commonly found in soil; in water that has been influenced by surface water and in human/animal waste.
The presence of total coliform bacteria shows that the water could be contaminated by environmental factors such as soil and dirt, with a likely presence of pathogens being present in the water. Total Coliform indicate: Biological contamination
Sign up for our newsletter!
 
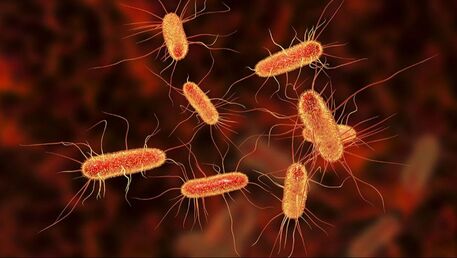
Escherichia coli (E.coli)
Source: https://www.istockphoto.com/sg
E.coli is a type of faecal coliform (bacteria) commonly found in the intestines of people and animals. E.coli is the best indicator of faecal pollution because it is generally not found in the environment.
As study by the World Health Organization (2018) shows that that at least 2 billion people are drinking from water sources at risk of faecal contamination. The presence of E.coli indicate an increased likelihood of the presence of pathogenic bacteria which is harmful to the body. E.coli can indicate: Biological contamination pH value
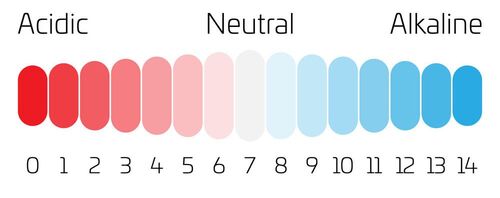
Source: https://www.vectorstock.com/royalty-free-vector/ph-scale-indicator-of-ph-value-expressing-rate-of-vector-22616573
pH value shows how acidic or alkaline the water is. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, consuming excessively alkaline or acidic water is harmful to our health.
Water with low pH (acidic, below 6.5) is corrosive and may contain dissolved heavy metals which will cause adverse health effects. Water with a high pH (alkaline, above 8.5) indicates that a high level of alkaline minerals is present. Water that is slightly alkaline does not seem to pose a health risk, but it can affect the taste and appearance of the water. For your further knowledge and information, here is everything you need know about alkaline water. pH value can indicate: Chemical contamination Suggestion: A Simple Water Test Kit to Identify the Water Quality
At the end of the day, knowing the constituents in your drinking water is the first step in ensuring that your water is safe to drink.
You can test the quality of your water using a laboratory or a portable water test kit. If you are travelling in remote areas such as disaster zones or rural areas, consider using our Water Test Kits to ensure that your water is safe to drink. Buy a portable test kit now for your next adventure!
Blog Author: Ze Yong Yeoh
Did you know, 525,000 children under 5 die from diarrhoeal diseases every year? Millions more fall ill due to water-borne diseases caused by the lack of access to clean drinking water.
*Please refer below for terms and conditions
|
Want more?Click below to see what other blog topics might peak your interest



Water Facts
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- About Us
- Products
- Solutions
- Resources
- Get Involved
-
Blog
- The Global Water Situation
-
Facts about Water
>
- Water supplies for crisis
- WaSH During Emergencies
- Well Water Cleaning and Filtration Guide: Southeast Asia
- Gravity-fed Water Systems: Water Purification and Filtration setups in Southeast Asia
- A Guide to Rural Rainwater Harvesting and Filtering
- Water Shortages and Their Effect on Children in Rural Schools
- WaSH Planning and Design Framework Resources for Indonesia and the Philippines
- Rural Community Water Supply: Water Systems in Villages
- Info on our Products
- Impact Stories
- Upcoming & Past Events
- Contact
- Store
- About Us
- Products
- Solutions
- Resources
- Get Involved
-
Blog
- The Global Water Situation
-
Facts about Water
>
- Water supplies for crisis
- WaSH During Emergencies
- Well Water Cleaning and Filtration Guide: Southeast Asia
- Gravity-fed Water Systems: Water Purification and Filtration setups in Southeast Asia
- A Guide to Rural Rainwater Harvesting and Filtering
- Water Shortages and Their Effect on Children in Rural Schools
- WaSH Planning and Design Framework Resources for Indonesia and the Philippines
- Rural Community Water Supply: Water Systems in Villages
- Info on our Products
- Impact Stories
- Upcoming & Past Events
- Contact
- Store
























.jpg)